Own your data
Everything in one place – your place. Use a storage account with a provider you trust, or set up your own storage server. Move house whenever you want. It's your data.
An open protocol for per-user storage on the Web
Everything in one place – your place. Use a storage account with a provider you trust, or set up your own storage server. Move house whenever you want. It's your data.
remoteStorage-enabled apps automatically sync your data across all of your devices, from desktop to tablet to smartphone, and maybe even your TV.
Use the same data across different apps. Create a to-do list in one app, and track the time on your tasks in another one. Say goodbye to app-specific data silos.
Most remoteStorage-enabled apps come with first-class offline support. Use your apps offline on the go, and automatically sync when you're back online.
remoteStorage is the first (and currently only) open standard to enable truly unhosted web apps. That means users are in full control of their precious data and where it is stored, while app developers are freed of the burden of hosting, maintaining and protecting a central database.
Developer hosts app and data,
user controls device.
Developer provides app and data,
user controls device.
Developer provides app only,
user controls device and data.
remoteStorage is a creative combination of existing protocols and standards. It aims to re-use existing technologies as much as possible, adding just a small layer of standardization on top to facilitate its usage for per-user storage with simple permissions and offline-capable data sync.
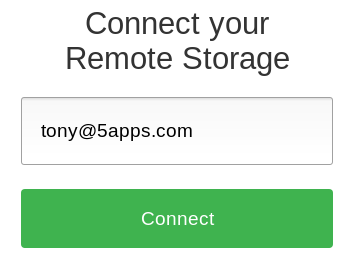
In order for apps to know where to ask permission and later actually sync user data, users give them a user address, basically like with E-Mail or Jabber/XMPP. With that address, apps retrieve storage information for the username on that domain/host.
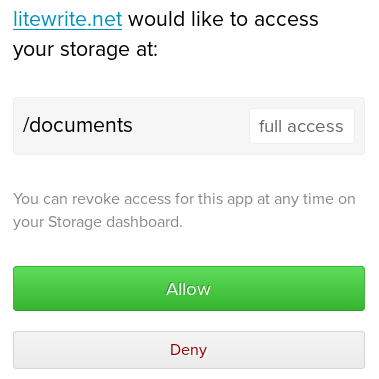
User data is scoped by so-called categories, which are essentially base directories, for which you can give apps read-only or read/write permission. Apps will use OAuth scopes to ask for access to one or more categories.
In the example screenshot, Litewrite
is asking for read/write access to the "documents" category, using
the OAuth scope documents:rw. If you allow access, the
app will retrieve a bearer token, with which it can read and write to
your storage, until you revoke that access on your server.
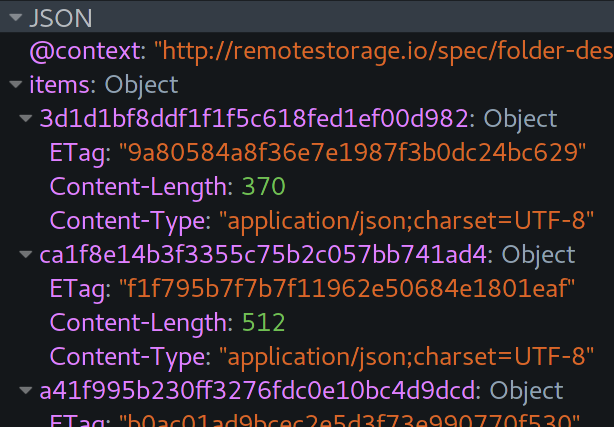
remoteStorage defines a simple key/value store for apps to save and retrieve data. The basic operations are GET/PUT/DELETE requests for specific files/documents.
In addition to that – and the only special feature aside from plain HTTP – there are directory listings, formatted as JSON-LD. They contain both the content type and size, as well as ETags, which can be used to implement sync mechanisms. The files and listings themselves also carry ETag headers for sync/caching and conditional requests.
remoteStorage is a grass-roots standard, developed completely in the open, by the community for the community. Countless individuals have contributed in one way or another over time, and we'd love to welcome you as one of them!
GitHub is where we collaborate on the protocol specification as well as all common source code.
Our community exchange and support site for everybody from users to developers to providers.
Many community members are hanging out in #remotestorage on Freenode. Say hi!
Follow @remotestorage_ on Twitter to receive updates on releases, events, apps, and related news.
Meet people in person at conferences, hackathons, camps, and other gatherings.
Want to make the world better by supporting RS in some way? Check out What can I do for remoteStorage? on our wiki.